Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic medical disorder, effecting joints, that has no known cure. However, a recent increase in research has led to the development of new treatments. The major aim of these treatments is to reduce disease activity and joint damage, and to enhance the quality of life for patients. It is important for patients to understand the course of the disease, what to expect, and how to manage it properly, so that they know what treatment to look for. The following are some of the treatment methods available for Rheumatoid Arthritis patients:
- Medicines
There are three general classes of drugs commonly used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs):While these won’t slow the progression of the disease or prevent further damage, they do help to reduce pain. Example of medicines that fall into this category are Aspirin, Advil, Motrin, Nuprin, Cataflam, Voltaren, and many others.
- Corticosteroids: These include medicines such as prednisone, which have both anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory properties. They can be administered orally, intravenously, intramuscularly, or even directly injected into the joint, depending on the needs of the patient. Some of the side effects include weight gain, high or increased blood pressure, and increased blood sure levels.
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Unlike NSAIDs, these help to reduce the effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis and are mostly prescribed when a diagnosis is first made to reduce the progression of the disease. Some of the drugs in this class are Methotrexate, Hydroxychloroquine, Sulfasalazine, Leflunomide, etc.
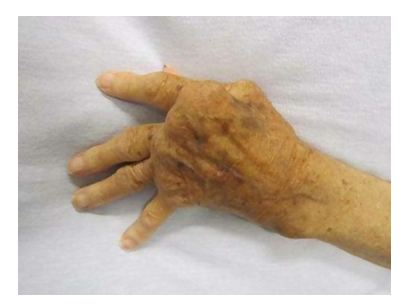
- Surgeries
Rheumatoid arthritis causes frequent paint and loss of joint mobility. Although these can be managed with drugs, they can also be improved surgically. Surgery can be risky however, so patients need to be properly informed of all possible outcomes and risks before they can consent to the procedure.
- Synovectomy: This is a surgical approach that involves removing the synovial tissue around a joint when it becomes inflamed and cannot be controlled by medication. It can be used to help with the pain and although the relief might be temporary, it helps.
- Arthroscopy: This procedure involves removing the damaged and inflamed tissue from the affected joints with the aim of restoring joint function and relieving pain especially in areas like the knee, hip, wrist, and elbow. It should be noted however that this does nothing to slow down the disease’s progression.
It is important for patients that suffer from Rheumatoid Arthritis to consult with their doctor before making any health decisions, as they will know the best options based on the development of their disease.
