Treatment for COPD
Introduction
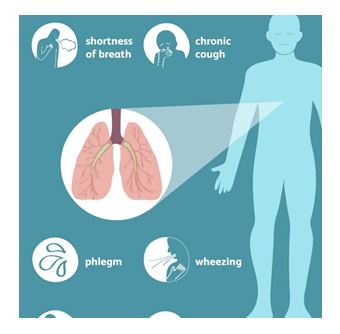
COPD is an acronym for chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease, which is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that reduces the amount
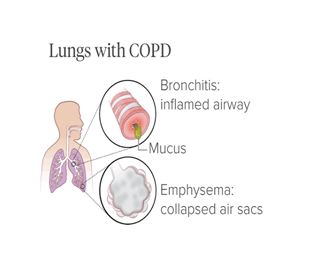
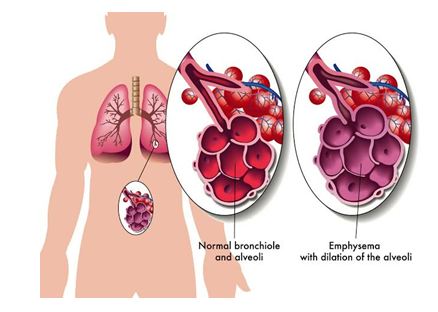
of air going into the lungs. Examples of COPD include emphysema, chronic
bronchitis, and refractory (non-reversible) asthma. It is characterized by
increasing breathlessness, cough, sputum production, and constant wheezing. It
is caused by prolonged exposure to irritating gases or particles, especially
from cigarette smoke. People with COPD are more susceptible to heart disease,
lung cancer, and other conditions.

According to research, COPD is one of the leading causes of hospitalizations in industrialized counties. In the United States, COPD causes 120,000 deaths per year.
Treatment for COPD
Although there is no cure for COPD and the damage is irreversible, there are treatments available that will ease symptoms, prevent complications, and generally slow the progression of the disease. These are some of the treatments available:
- Medication
Bronchodilators:COPD blocks airways from getting as much oxygen as they need. Bronchodilators, like Theophylline, are often prescribed to widen the airways and ease breathing. There are two types of bronchodilators: temporary relief and long lasting. Both types can be taken on their own or in combination with an inhaler or nebulizer. If there is a thick mucus blocking your airway, a doctor can prescribe something like Carbocisteine. to clear it.
Nebulized medication: Nebulizers turn liquid medication into a fine mist that can be inhaled through a mouthpiece or facemask allowing large doses of medications to be delivered at once. This method is typically used in cases where inhalers and standard medications are ineffective.
Oxygen therapy: When blood oxygen levels get too low, the body doesn’t function properly. Patients are often given supplemental oxygen through a mask to help them get a higher rate of oxygen with each breath.
Surgery :Surgery is carried out when other treatments are not working or when the patient seems to be rapidly deteriorating. There are different kinds of surgery that can be done including:
- Bullectomy: This is a surgical procedure where small, oxygen depleted, portions of the lungs, called bulla, are removed.
- Lung volume reduction surgery: In this procedure, the damaged upper lung tissues are removed.
- Lung transplantation: If possible, the lungs can be replaced with a healthy pair.
Not all treatments work for everyone, so it is important that you consult with your doctor to find out which treatment would be best for you. Factors will include the extent of damage the COPD has caused your lungs and other organs, your age, and your overall health.
